view 的事件传递
在官网里面:
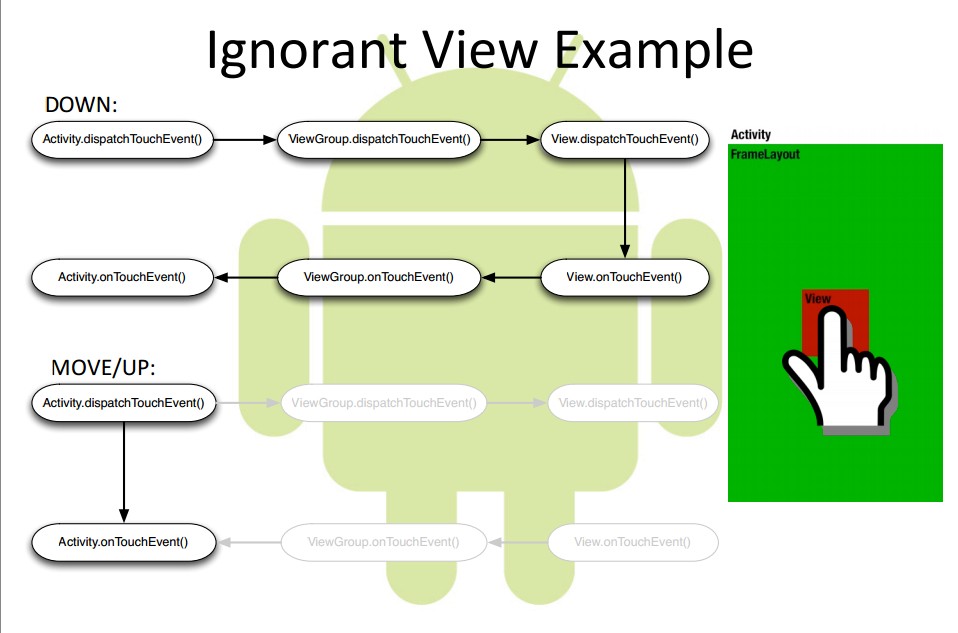
- view 不处理事件流程图
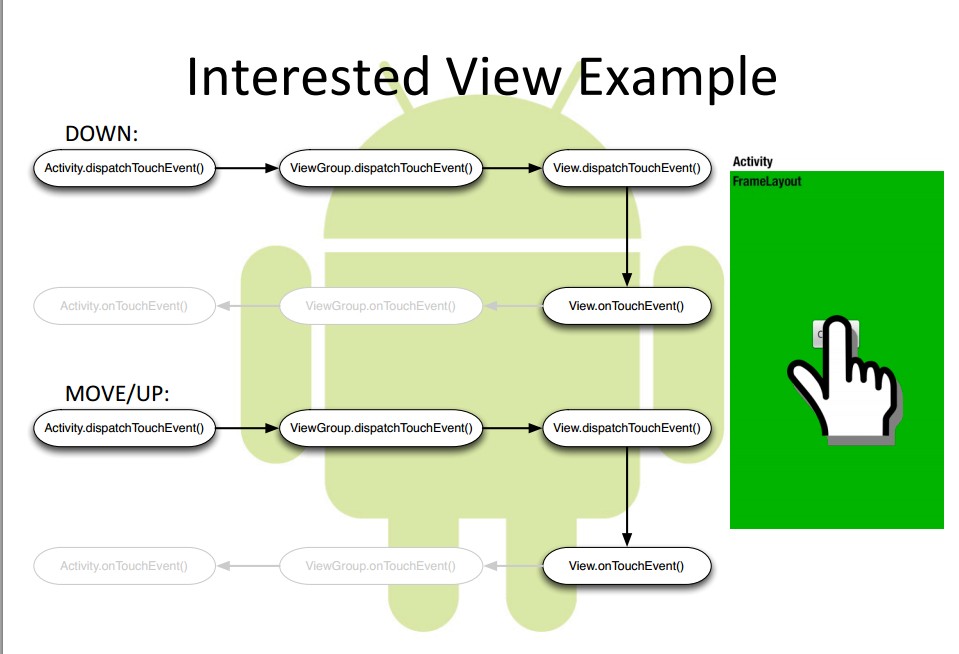
- view处理事件流程图
基础知识:
所有touch事件都被封装成MotionEvent对象
对事件的处理有三类,分别是:
- 传递: dispatchTouchEvent()
- 拦截: onInterceptTouchEvent()
- 消费: onTouchEvent() 和onTouchListener
在源码里面,会先对onTouchListener进行判断,才决定要不要传递给onTouchEvent,
所以onTouchListener会优先于onTouchEvent().
传递流程:
事件从Activity.dispatchTouchEvent()开始传递,只要没有被停止或拦截,
从最上层的View(ViewGroup)开始一直往下(子View)传递,子View可以通过onTouchEvent()对事件进行处理。
viewgroup(传递)—->view, 同时viewgroup可以通过onInterceptTouchEvent()对事件做拦截。
如果从上向下传递的过程中一直为停止,且最底层没有消费事件,事件会向上传递,这是父view可以
进行消费,如果还是没有消费,最后会到activity的onTouchEvent().
执行顺序是:
Activity.dispatchTouchEvent()
ViewGroup.dispatchTouchEvent()
View.dispatchTouchEvent()
View.onTouchEvent()
ViewGroup.onTouchEvent()
Activity.onTouchEvent()
onInterceptTouchEvent 返回false,则后续再来的事件(比如ACTION_UP)会
继续传递给子view的onTouchEvent;
onInterceptTouchEvent 返回true,则后续再来的事件(比如ACTION_UP)就
不会传递给子view.
view的onTouchEvent返回true,则表示后续事件已经消化干净,viewgroup的
onTouchEvent就不会被调用,否则相反。
onTouchEvent()—->ACTION_DOWN时,返回false,则后续的手势动作都不会
传递进这个方法(ViewGroup和View一样).
viewgroup的onTouchEvent()—->返回true,则后续手势都不会传递给onInterceptTouchEvent()
而是在ViewGroup的onTouchEvent()中注意处理。
view 树的绘制流程
流程图:
view绘制流程函数调用链。

树的遍历是有序的,由父视图到子视图,每一个viewgroup负责测绘它的所有子视图,而最底层的view会负责自身回测。
具体分析
measure 过程是由measure(int, int)方法发起,从上到下有序的测量view,在measure过程的最后,
每个视图存储了自己的大小和测量规格,layout过程由layout(int, int, int)方法发起,
也是自上而下。在该过程中,每个父视图会根据measure过程得到的尺寸来摆放自己的子视图。
measure 过程会为一个View及所有子节点的 mMeasuredWidth 和 mMeasuredHeight 变量赋值,
该值可以通过getMeasureWidth()和getMeasureHeight()得到。而且这两个值必须在父视图约束范围之内
这样才可以保证所有的父视图都接收所有子视图的测量。
measure过程传递尺寸的两个类
- ViewGroup.LayoutParams(view 自身的布局参数)
- MeasureSpecs类(父视图对子视图的测量要求)
ViewGroup.LayoutParams
这个类很常见,用来指定视图的高度和宽度等参数。对于视图的宽和高:
- 具体值
- MATCH_PARENT 表示子视图希望和父视图一样大(不包含padding值)
- WRAP_CONTENT 表示视图为正好能包裹其内容大小(包含padding值)
ViewGroup 的子类有其对应的 ViewGroup.LayoutParams 的子类。
有时我们需要使用 view.getLayoutParams() 方法获取一个视图 LayoutParams ,
然后进行强转,但由于不知道其具体类型,可能会导致强转错误。其实该方法就是
得到其所在父视图类型的 LayoutParams,比如 View 的父控件为 RelativeLayout,
那么得到的 LayoutParams 类型就为 RelativeLayoutParams。 这里需要很特别的注意,在强转时可能会造成错误!!!
MeasureSpecs
测量规格,包含测量要求和尺寸的信息,有三种模式:
- UNSPECIFIED
父视图不对子视图有任何约束,它可以达到所期望的任意尺寸。
比如ListView、ScrollView,一般自定义View中用不到 EXACTLY
父视图为子视图指定一个确切的尺寸,而且无论子视图期望多大,
它都必须在该指定大小的边界内,对应的属性为 match_parent 或具体指,
比如 100dp,父控件可以通过MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec)直接得到子控件的尺寸。AT_MOST
父视图为子视图指定一个最大尺寸。子视图必须确保它自己所有子视图
可以适应在该尺寸范围内,对应的属性为 wrap_content,在这种模式下,
父控件无法确定子 View 的尺寸,只能由子控件自己根据需求去计算自己的尺寸
measure 核心方法
measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
该方法定义在view.java类中,为final类型,不可被复写,但 measure 调用链
最终会回调 View/ViewGroup 对象的 onMeasure(),因此自定义视图时,只需要重写onMeasure()onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
该方法就是我们自定义视图中实现测量逻辑的方法,该方法的参数是父视图
对子视图的 width 和 height 的测量要求,在自定义视图中,要根据该
widthMeasureSpec 和 heightMeasureSpec 计算视图的 width 和 height,
不同的模式处理方式不同。setMeasuredDimension()
测量阶段终极方法,在 onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) 方法中调用,
将计算得到的尺寸,传递给该方法,测量阶段即结束。该方法也是必须要调用的方法,否则会报异常。
在自定义视图里面,不需要关心系统复杂的 Measure 过程的,只需调用setMeasuredDimension()
设置根据 MeasureSpec 计算得到的尺寸。
取 ViewGroup 的 measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
对对复合 View 的 Measure 流程做一个分析: MeasureChild 的方法调用流程图:
源码分析
/**
* 请求所有子 View 去 measure 自己,要考虑的部分有对子 View 的测绘要求 MeasureSpec 以及其自身的 padding
* 这里跳过所有为 GONE 状态的子 View ,最繁重的工作是在 getChildMeasureSpec 方法中处理的
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec 对该 View 的 width 测绘要求
* @param heightMeasureSpec 对该 View 的 height 测绘要求
*/
protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int size = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) {
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();//获取Child的LayoutParams
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,// 获取 ChildView的widthMeasureSpec
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,// 获取 ChildView的heightMeasureSpec
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
/**
* 该方法是 measureChildren 中最繁重的部分,为每一个 ChildView 计算出自己的 MeasureSpec。
* 目标是将 ChildView 的 MeasureSpec 和 LayoutParams 结合起来去得到一个最合适的结果。
*
* @param spec 对该 View 的测绘要求
* @param padding 当前 View 在当前唯独上的 paddingand,也有可能含有 margins
*
* @param childDimension 在当前维度上(height或width)的具体指
* @return 子视图的 MeasureSpec
*/
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
.........
// 根据获取到的子视图的测量要求和大小创建子视图的MeasureSpec
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
/**
*
* 用于获取 View 最终的大小,父视图提供了宽、高的约束信息
* 一个 View 的真正的测量工作是在 onMeasure(int, int) 中,由该方法调用。
* 因此,只有 onMeasure(int, int) 可以而且必须被子类复写
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec 在水平方向上,父视图指定的的 Measure 要求
* @param heightMeasureSpec 在竖直方向上,控件上父视图指定的 Measure 要求
*
*/
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
...
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
...
}
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
layout相关概念及核心方法
首先要明确的是,子视图的具体位置都是相对于父视图而言的,view的onLayout()为空实现,
而 ViewGroup 的 onLayout 为 abstract 的,所以,如果自定义view要继承ViewGroup,
必须实现onLayout函数。
在layout过程中,子视图会调用getMeasuredWidth()和getMeasuredHeight()获取到measure
过程得到的 mMeasuredWidth 和 mMeasuredHeight,作为自己的 width 和 height
然后调用每一个子视图的layout(l, t, r, b)函数,来确定每一个子视图的位置
linearlayout的onLayout源码分析
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
layoutVertical(l, t, r, b);
} else {
layoutHorizontal(l, t, r, b);
}
}
/**
* 遍历所有的子 View,为其设置相对父视图的坐标
*/
void layoutVertical(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child == null) {
childTop += measureNullChild(i);
} else if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {//不需要立即展示的View设置为GONE可加快绘制
final int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();//measure过程确定的Width
final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();//measure过程确定的height
...确定 childLeft、childTop 的值
setChildFrame(child, childLeft, childTop + getLocationOffset(child),
childWidth, childHeight);
}
}
}
private void setChildFrame(View child, int left, int top, int width, int height) {
child.layout(left, top, left + width, top + height);
}
View.java
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
...
setFrame(l, t, r, b)
}
/**
* 为该子 View 设置相对其父视图上的坐标
*/
protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
...
}
绘制流程相关概念及核心方法
与draw过程的相关的函数:
View.draw(Canvas canvas):
ViewGroup 并没有复写此方法,所以所有的视图最终都是调用 View 的 draw
进行绘制的。在自定义的视图中,不应该复写该方法,而是复写onDraw(Canvas)方法进行绘制
如果自定义的视图一定要复写该方法,请先调用super.draw(canvas)完成系统的绘制,再进行自定义绘制View.onDraw():
View的onDraw(Canvas)默认是空实现,自定义绘制过程需要复写的方法,绘制自身的内容。
dispatchDraw() 发起对子视图的绘制
View中默认是空实现,ViewGroup 复写了dispatchDraw()来对其子视图进行绘制,
该方法我们不用去管,自定义的 ViewGroup 不应该对dispatchDraw()进行复写。
绘制流程图:
View.draw(Canvas) 源码分析
/**
* Manually render this view (and all of its children) to the given Canvas.
* The view must have already done a full layout before this function is
* called. When implementing a view, implement
* {@link #onDraw(android.graphics.Canvas)} instead of overriding this method.
* If you do need to override this method, call the superclass version.
*
* @param canvas The Canvas to which the View is rendered.
*
* 根据给定的 Canvas 自动渲染 View(包括其所有子 View)。在调用该方法之前必须要完成 layout。当你自定义 view 的时候,
* 应该去是实现 onDraw(Canvas) 方法,而不是 draw(canvas) 方法。如果你确实需要复写该方法,请记得先调用父类的方法。
*/
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
/ * Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed
* in the appropriate order:
*
* 1. Draw the background if need
* 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading
* 3. Draw view's content
* 4. Draw children (dispatchDraw)
* 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers
* 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance)
*/
// Step 1, draw the background, if needed
if (!dirtyOpaque) {
drawBackground(canvas);
}
// skip step 2 & 5 if possible (common case)
final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;
if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) {
// Step 3, draw the content
if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas);
// Step 4, draw the children
dispatchDraw(canvas);
// Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars)
onDrawScrollBars(canvas);
if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas);
}
// we're done...
return;
}
// Step 2, save the canvas' layers
...
// Step 3, draw the content
if (!dirtyOpaque)
onDraw(canvas);
// Step 4, draw the children
dispatchDraw(canvas);
// Step 5, draw the fade effect and restore layers
// Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars)
onDrawScrollBars(canvas);
}
由上面的处理过程,我们也可以得出一些优化的小技巧:
当不需要绘制 Layer 的时候第二步和第五步会跳,。因此在绘制的时候,
能省的layer尽可省,可以提高绘制效率.
ViewGroup.dispatchDraw() 源码分析
dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas){
...
if ((flags & FLAG_RUN_ANIMATION) != 0 && canAnimate()) {//处理ChildView的动画
final boolean buildCache = !isHardwareAccelerated();
for (int i = 0; i < childrenCount; i++) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE) {//只绘制 Visible 状态的布局,因此可以通过延时加载来提高效率
final LayoutParams params = child.getLayoutParams();
attachLayoutAnimationParameters(child, params, i, childrenCount);// 添加布局变化的动画
bindLayoutAnimation(child);//为Child绑定动画
if (cache) {
child.setDrawingCacheEnabled(true);
if (buildCache) {
child.buildDrawingCache(true);
}
}
}
}
final LayoutAnimationController controller = mLayoutAnimationController;
if (controller.willOverlap()) {
mGroupFlags |= FLAG_OPTIMIZE_INVALIDATE;
}
controller.start();// 启动 View 的动画
}
// 绘制 ChildView
for (int i = 0; i < childrenCount; i++) {
int childIndex = customOrder ? getChildDrawingOrder(childrenCount, i) : i;
final View child = (preorderedList == null)
? children[childIndex] : preorderedList.get(childIndex);
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null) {
more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime);
}
}
...
}
protected boolean drawChild(Canvas canvas, View child, long drawingTime) {
return child.draw(canvas, this, drawingTime);
}
/**
* This method is called by ViewGroup.drawChild() to have each child view draw itself.
* This draw() method is an implementation detail and is not intended to be overridden or
* to be called from anywhere else other than ViewGroup.drawChild().
*/
boolean draw(Canvas canvas, ViewGroup parent, long drawingTime) {
...
}
drawChild(canvas, this, drawingTime)
直接调用了 View 的child.draw(canvas, this,drawingTime)方法,文档中也说明了,
除了被ViewGroup.drawChild()方法外,你不应该在其它任何地方去复写或调用该方法,
它属于 ViewGroup。而View.draw(Canvas)方法是我们自定义控件中可以复写的方法,
具体可以参考上述对view.draw(Canvas)的说明。
从参数中可以看到,child.draw(canvas, this, drawingTime) 肯定是处理了和父视图相关的逻辑
但 View 的最终绘制,还是 View.draw(Canvas)方法。invalidate()
请求重绘 View 树,即 draw 过程,假如视图发生大小没有变化就不会调用layout()过程
并且只绘制那些调用了invalidate()方法的 View。requestLayout()
当布局变化的时候,比如方向变化,尺寸的变化,会调用该方法,在自定义的视图中,
如果某些情况下希望重新测量尺寸大小,应该手动去调用该方法,
它会触发measure()和layout()过程,但不会进行 draw。
chenzhao@hustunique.com